Key findings
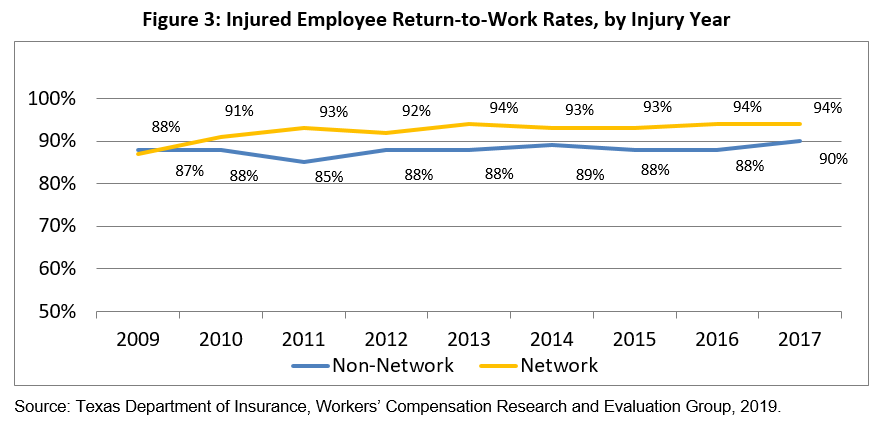
- Return-to-work rates for network injured employees consistently higher than for non-network injured employees after 2009.
- Return-to-work rate for network injured employees averaged 90 percent before formulary took effect and 94 percent after.
- Return-to-work rate for non-network injured employees averaged 87 percent before formulary took effect and 90 percent after.
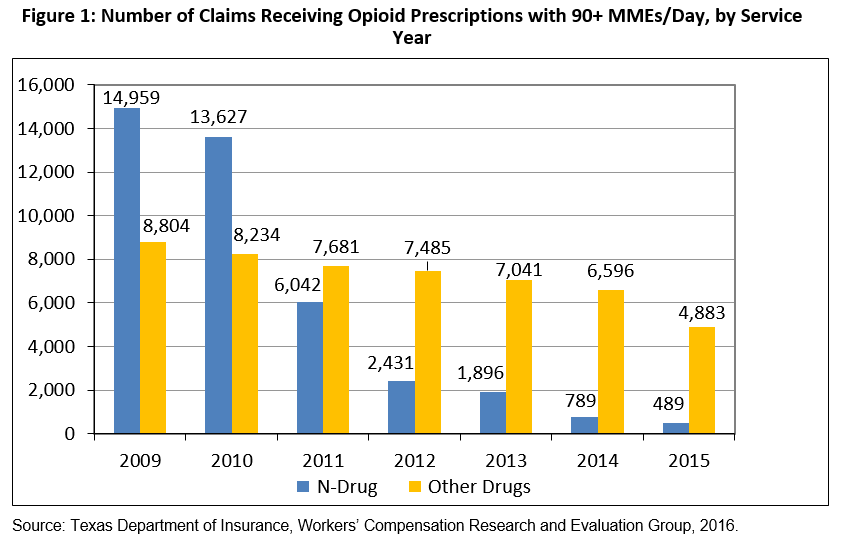
- Mental functioning scores for network injured employees averaged 51.2 before and 51.6 after the formulary went into effect. These scores were higher in 2016 than in any other year since implementing the formulary.
- Mental functioning scores for non-network injured employees averaged 50.0 before and 49.6 after the formulary went into effect. These scores were higher in 2016 than in any other year since implementing the formulary.
- Mental functioning scores for network injured employees were consistently higher than for the non-network injured employees and the U.S. population.
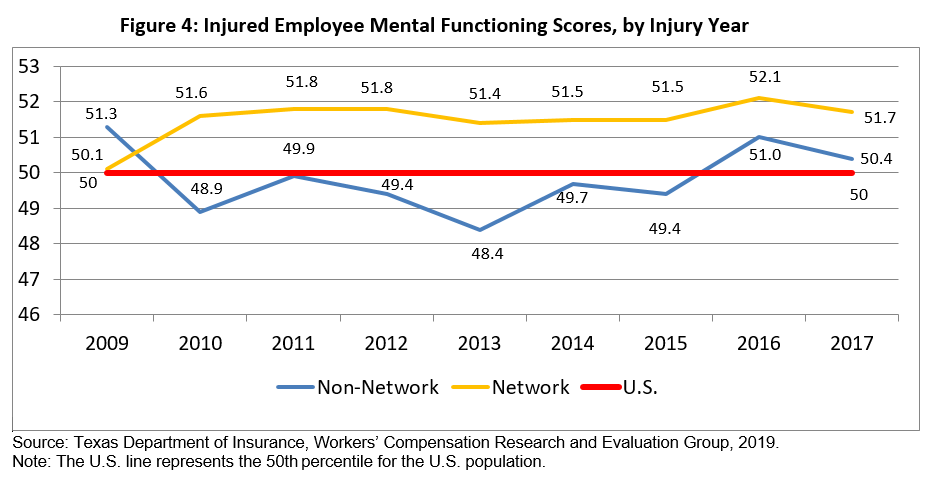
- Mental functioning scores for network injured employees averaged 51.2 before and 51.6 after the formulary went into effect. These scores were higher in 2016 than in any other year since implementing the formulary.
- Mental functioning scores for non-network injured employees averaged 50.0 before and 49.6 after the formulary went into effect. These scores were higher in 2016 than in any other year since implementing the formulary.
- Mental functioning scores for network injured employees were consistently higher than for the non-network injured employees and the U.S. population.
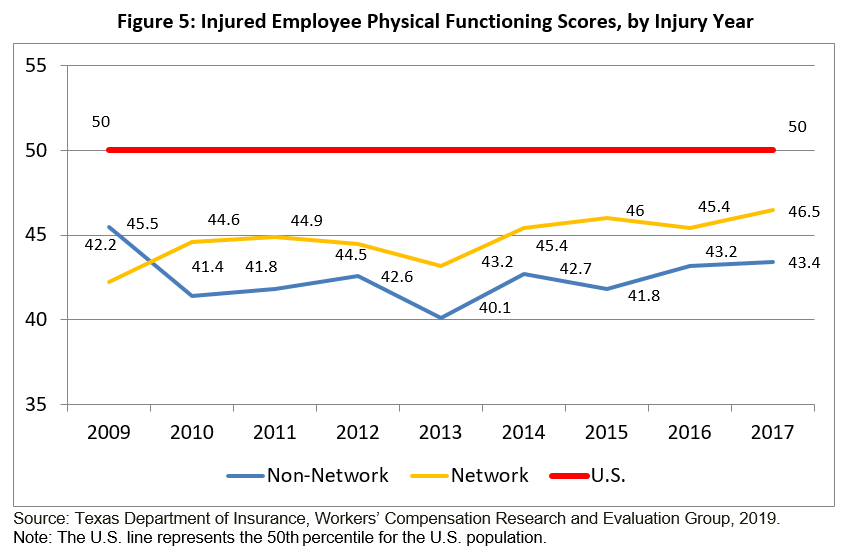
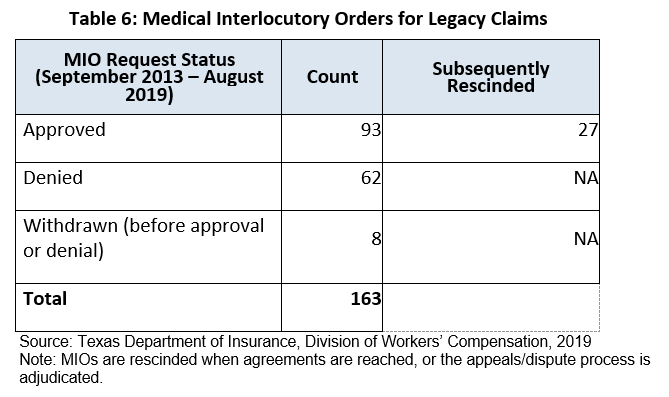
DWC implemented the pharmacy closed formulary for legacy claims in 2013.
DWC created a process to allow a prescribing doctor or pharmacy to obtain a medical interlocutory order (MIO) when an insurance carrier denies preauthorization of previously prescribed drugs. An MIO allows an injured employee to continue using the drug throughout the duration of the dispute process.
As of September 2019, 60 percent of the Medical Interlocutory Orders (MIO) requested were approved.