Every two minutes, preventable accidents cause one death and 236 injuries, according to the National Safety Council. Identifying hazards is the foundation of a safe workplace. Look at a job, task, or situation, and ask, “Is there anything here that could hurt someone or damage something?”
When employers and employees ask this question to improve safety in their facility, they are looking for any practice, behavior, or physical condition that may cause harm and ways to eliminate or control it. This is known as a Job Hazard Analysis and is one of the most effective means to prevent injuries and illnesses. These are the basic steps:
1 Identify job tasks.
Break down each task employees perform at a work site into individual steps.
2 Find potential hazards.
Look at the job, materials, equipment, tools, and environment for possible hazards and situations that may cause harm. Get input from all employees. Different people may notice different safety concerns. (See DWC’s Job Hazard Analysis Fact Sheet for possible workplace hazards.)
3 Assess the risks.
Evaluate the level of risk for each identified hazard. Prioritize each on a “worst first” basis. Consider its effects on you, your coworkers, the property, the community, and the environment.
4 Create control measures.
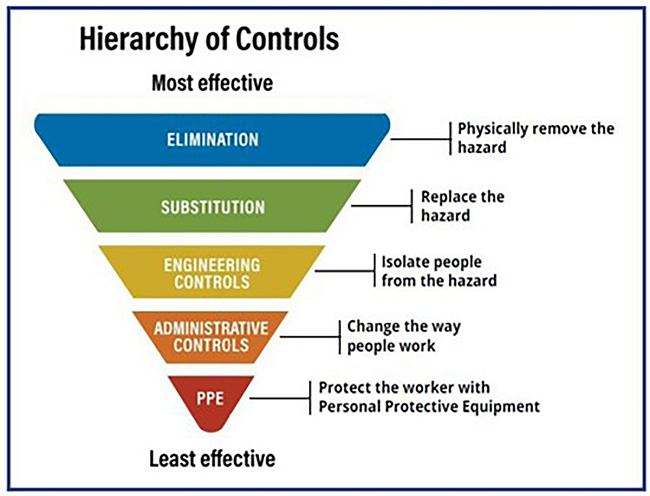
Find ways to control identified hazards by:
- physically removing the hazard (elimination);
- replacing the hazard (substitution);
- isolating people from the hazard (engineering controls);
- changing the way people work (administrative controls); and
- protecting workers with personal protective equipment (PPE).
5 Communicate and monitor the program.
Inform employees, supervisors, and other stakeholders about the identified hazards and control measures. Regularly review the program and assess the results. Make changes as needed and any time a job condition or physical effect changes.
If your company would like free, confidential assistance identifying and eliminating occupational hazards in your workplace or complying with OSHA standards, contact one of DWC’s Occupational Safety and Health Consultation (OSHCON) professionals at 800-252-7031, option 2, or OSHCON@tdi.texas.gov. For more information, visit www.txoshcon.com.
